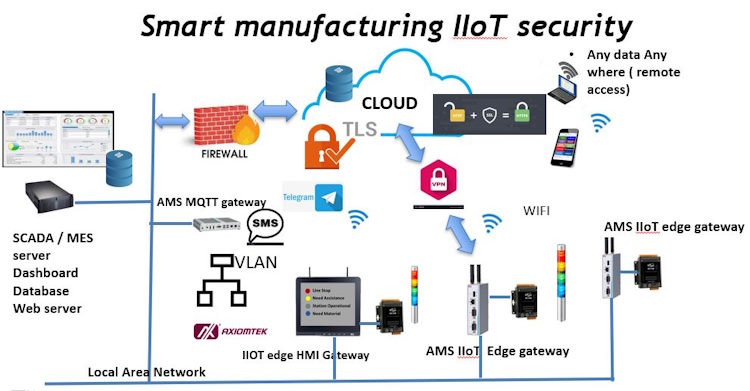
What are challenges in digital transformation in the building of smart manufacturing.
The digital transformation in manufacturing brings numerous benefits, but it also presents significant challenges to data security. Here are some key challenges:
Increased Attack Surface: As manufacturing processes become more interconnected through digital technologies like IoT devices, cloud computing, and automation systems, the attack surface for potential cyber threats expands. Each new endpoint or connection represents a potential entry point for attackers.
Complexity of Systems: Modern manufacturing facilities often comprise a complex ecosystem of interconnected systems and devices, including legacy equipment that may not have been designed with security in mind. Managing the security of such a complex environment can be challenging.
Data Protection: Manufacturing involves the collection and processing of sensitive data, including intellectual property, trade secrets, and personally identifiable information (PII). Ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of this data is crucial to protecting business interests and complying with regulations.
Supply Chain Risks: Manufacturers often rely on extensive supply chains involving multiple vendors and partners. Each entity in the supply chain represents a potential security risk, as vulnerabilities in one part of the chain can have ripple effects throughout the entire ecosystem.
Insider Threats: Insider threats, whether intentional or unintentional, pose a significant risk to data security. Employees, contractors, or partners with access to sensitive systems and information may inadvertently compromise security through negligence or deliberately engage in malicious activities.
Rapid Technological Advancements: The pace of technological innovation in manufacturing is accelerating, introducing new tools and capabilities that may outpace existing security measures. Keeping up with these advancements and ensuring that security measures remain effective can be a challenge.
Regulatory Compliance: Manufacturing companies are subject to various regulatory requirements regarding data security and privacy, such as GDPR in Europe or CCPA in California. Compliance with these regulations adds an additional layer of complexity to data security efforts.
Cybersecurity Skills Gap: The shortage of skilled cybersecurity professionals poses a significant challenge for manufacturing companies. Recruiting and retaining qualified personnel to design, implement, and manage effective security measures can be difficult.
Addressing these challenges requires a multi-faceted approach that includes implementing robust security technologies, establishing clear policies and procedures, providing ongoing training and awareness programs for employees, collaborating with partners and suppliers to enhance security throughout the supply chain, and staying abreast of evolving threats and regulatory requirements.
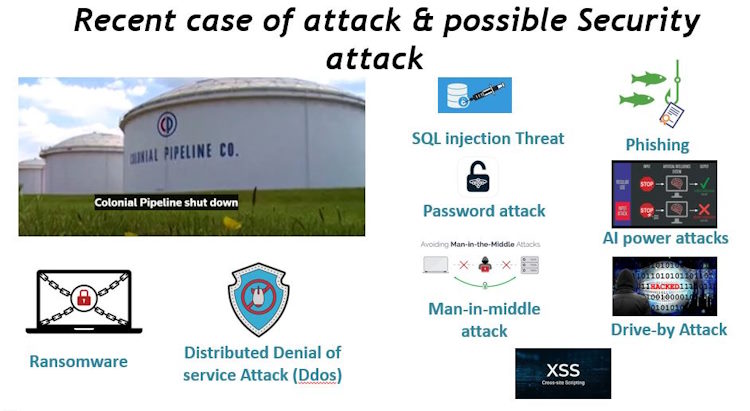
Cybersecurity threats are diverse and constantly evolving, but here’s an overview of some common ones:
Phishing Attacks: Deceptive attempts to obtain sensitive information (such as usernames, passwords, and credit card details) by impersonating a trustworthy entity.
Malware: Malicious software designed to disrupt, damage, or gain unauthorized access to computer systems. This includes viruses, worms, trojans, ransomware, and spyware.
Social Engineering: Manipulating individuals into divulging confidential information or performing actions that compromise security, often through psychological manipulation or impersonation.
Denial-of-Service (DoS) and Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) Attacks: Overloading a system or network with excessive traffic to disrupt its normal functioning, making it inaccessible to legitimate users.
Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) Attacks: Intercepting and possibly altering communication between two parties without their knowledge, allowing attackers to eavesdrop or manipulate data.
SQL Injection: Exploiting vulnerabilities in web applications to inject malicious SQL code, enabling attackers to access, modify, or delete data stored in databases.
Credential Theft: Unauthorized acquisition of usernames, passwords, or other authentication credentials, often through phishing, keylogging, or exploiting weak authentication mechanisms.
Cryptojacking: Illicit use of someone else’s computing resources to mine cryptocurrency without their consent, often accomplished through malware or compromised websites.
IoT (Internet of Things) Vulnerabilities: Exploiting security weaknesses in connected devices and systems, including smart home appliances, industrial sensors, and medical devices, to gain unauthorized access or disrupt operations.
Data Breaches: Unauthorized access, disclosure, or theft of sensitive or confidential data, which can result in financial loss, reputational damage, and regulatory penalties.
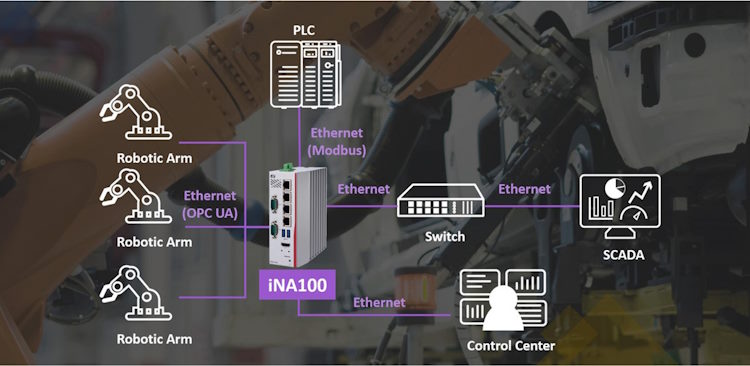
Protecting Operational Technology (OT) networks with firewalls involves implementing specialized firewall configurations tailored to the unique requirements and characteristics of OT environments. Here’s how firewalls can be used to enhance security in OT networks:
Segmentation: Firewalls can be deployed to segment the OT network into zones based on logical groupings of devices or functions. For example, separating critical infrastructure devices (such as industrial control systems) from less critical systems (such as employee workstations). This segmentation helps contain the impact of security incidents and restrict unauthorized access to sensitive OT assets.
Access Control: Firewalls enforce access control policies to regulate traffic flow between different zones within the OT network. By defining rules based on source and destination IP addresses, ports, protocols, and application-layer information, firewalls can permit or deny communication as necessary to prevent unauthorized access, limit exposure to external threats, and ensure compliance with security policies.
Intrusion Detection and Prevention: Next-generation firewalls (NGFWs) equipped with intrusion detection and prevention system (IDPS) capabilities can monitor OT network traffic in real-time for signs of suspicious or malicious activity. These systems use signature-based detection, anomaly detection, and behavioral analysis techniques to identify and block known and unknown threats, such as malware, exploits, and unauthorized access attempts.
Deep Packet Inspection: Firewalls with deep packet inspection (DPI) capabilities can inspect the content of network packets at the application layer to detect and block malicious payloads, command-and-control communications, and other security threats hidden within encrypted traffic. This helps protect OT systems from advanced threats that may evade traditional security mechanisms.
VPN and Remote Access Security: Firewalls can secure remote access to OT networks by providing Virtual Private Network (VPN) services and enforcing strong authentication, encryption, and access control policies for remote users and devices. This helps protect sensitive OT assets from unauthorized access and cyber attacks originating from external networks, including the internet.
Logging and Monitoring: Firewalls generate logs and alerts that provide visibility into network activity, security events, and policy violations within the OT environment. By monitoring firewall logs and analyzing security events in real-time, organizations can identify potential security incidents, investigate suspicious behavior, and respond promptly to mitigate risks and minimize the impact of cyber attacks on OT systems.
Overall, firewalls play a crucial role in safeguarding OT networks by providing network segmentation, access control, threat detection and prevention, secure remote access, and monitoring capabilities tailored to the unique requirements of industrial control systems and critical infrastructure environments.
To watch our live session on youtube channel:-
