5G AIOT and Dataspace integration

AIoTmission brought to you the AIOT integration with Dataspace this round in the ” Sembang AIoT session”
In a very layman’s terms, the Dataspace is just like a physical Library or a warehouse where you keep all your books and goods and you have a way to manage them well with a good retrieval, storing, and use method. In the digital terms, dataspace can be of the data you store in the computers, server and storage devices where when it is connected with the internet, it allows reading, writing, and process within the environment. Expanding this part, it can be located at the cloud or data lake at the cloud. The contents can be of any of of files formats from any applications, medial files and databases.
In simple terms, think of a Dataspace as a digital library or storage room. It’s a place where you keep all your digital “books” and “items,” which means all kinds of data, organized so you can easily find, use, and store them again. Just like in a physical library or warehouse, there’s a system in place to help you manage everything smoothly. In the world of technology, this “Dataspace” refers to the data you save on computers, servers, and other storage devices. Once connected to the internet, this setup enables you to read, write, and process data within this digital environment. It can stretch even further, reaching into the cloud or becoming part of a data lake housed in the cloud. This digital collection can include anything from various file formats generated by different applications, media files, to databases.
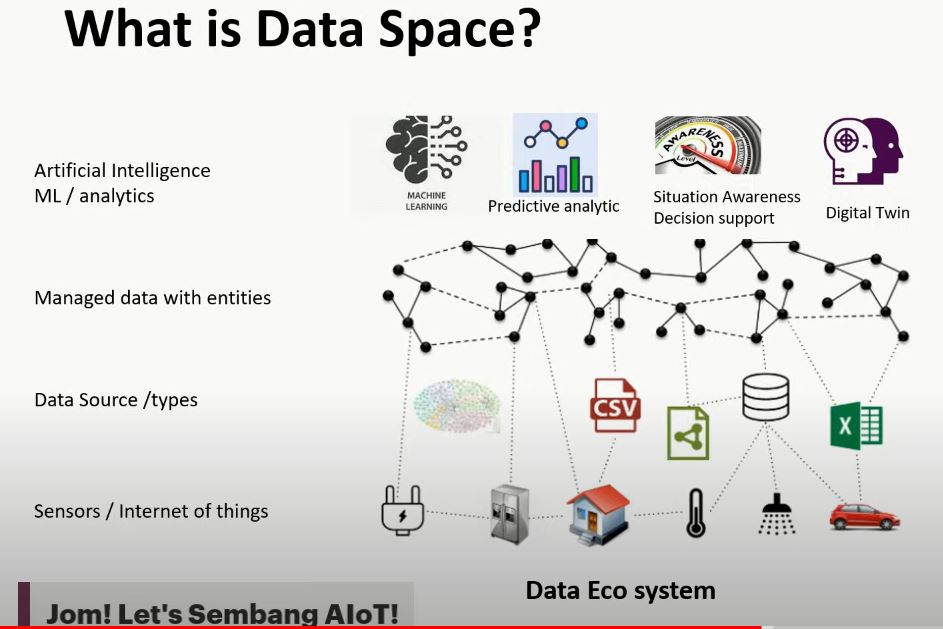
Dataspace is formed with the connected infrastructure called Data Eco system. There are several layers in the Eco System. From the very low level of Sensors or IOT sensors that forms the data source that piped into the managed data entities to the applications and processing, AI and IoT play a significant roles in it.
Components of a Dataspace Ecosystem
Technological Infrastructure: This includes all hardware and software components, such as data storage systems (databases, data lakes, cloud storage), data processing tools, and networking systems that support the storage, processing, and movement of data.
Data Governance and Management: Policies, standards, and procedures that ensure data quality, security, privacy, and compliance. This aspect also covers the management of metadata, which facilitates data discovery and understanding.
Integration and Interoperability Tools: Software and platforms that enable the seamless connection and interaction between different data sources and formats. These tools help in mapping, transforming, and querying data across the ecosystem without requiring uniformity.
Analytics and Processing Capabilities: Advanced analytics, machine learning models, and processing tools that can work with diverse data types to generate insights, forecasts, and reports.
User Access and Collaboration: Interfaces and protocols that allow various stakeholders, including data scientists, analysts, and business users, to access, share, and collaborate on data insights within the ecosystem.
Security and Compliance Mechanisms: Systems and practices that protect data integrity, confidentiality, and compliance with legal and regulatory requirements.
Importance of a Dataspace Ecosystem
An effective dataspace ecosystem enables organizations to harness the full potential of their data assets by breaking down silos and promoting a more integrated and collaborative approach to data management. It supports decision-making processes, innovation, and operational efficiency by providing a holistic view of the organization’s data landscape. Additionally, it enhances agility by allowing for the rapid integration of new data sources and technologies, adapting to changing business needs and technological advancements.
Challenges in Building a Dataspace Ecosystem
Creating a dataspace ecosystem involves addressing several challenges, including the integration of heterogeneous data sources, ensuring data quality and consistency, managing data privacy and security, and fostering a culture that values data-driven decision-making. Successful implementation requires a strategic approach, involving both technological solutions and organizational change management.
In summary, a dataspace ecosystem represents an advanced model for data management, aiming to create a cohesive, efficient, and flexible environment for leveraging data across an organization or community.
Now, how does this relate to AI (Artificial Intelligence) and IoT (Internet of Things)?
AI and Dataspace
AI is like a smart librarian in this virtual library. It doesn’t just help you find things but also understands what you might need even before you ask. For example, based on what you’ve looked for in the past, it can suggest new information or make connections between different pieces of data to help you make decisions. This is possible because the dataspace organizes data in a way that AI can easily access and learn from it, helping the AI to get smarter over time and provide you with more personalized and accurate assistance.
IoT and Dataspace
Imagine if every book and item in the library could talk and tell you exactly where it is, how it’s feeling (like if a device is overheating), or even if it’s about to run out of battery. That’s what IoT devices do in the dataspace. These devices, like smart thermostats, fitness trackers, and even smart fridges, are constantly sending information to the dataspace. This data can tell you (and the smart librarian AI) what’s happening in the real world, in real-time. So, the dataspace not only stores this information but also helps make sense of it, allowing you to control these devices better or get insights into your daily activities and environment.
The Connection
The magic happens when AI and IoT work together within the dataspace. AI uses the vast amount of data generated by IoT devices to learn patterns, make predictions, and automate tasks. For instance, an AI might analyze the data from smart home devices to optimize energy use, making your home more comfortable while saving on electricity bills.
In layman’s terms, the dataspace is the backbone that supports AI and IoT by organizing and storing all the data they need and produce. It’s like the brain and memory for these technologies, enabling them to work smarter and make our lives easier and more connected.

Imagine 5G mobile communication as the super-fast express delivery service for the digital world, significantly impacting how data is moved, accessed, and utilized within the dataspace. Here’s how 5G plays a pivotal role:
Speed and Bandwidth
5G offers incredibly fast data speeds and more bandwidth compared to its predecessors. This means that information can travel back and forth between devices, servers, and the internet much quicker. In the context of a dataspace, which relies on the timely and efficient exchange of data, 5G ensures that even the most data-intensive tasks are completed smoothly and swiftly. This is akin to upgrading from a bicycle courier to a fleet of high-speed delivery drones for your data.
Reduced Latency
Latency refers to the delay before a transfer of data begins following an instruction for its transfer. 5G dramatically reduces this delay, making real-time data exchange and processing a reality. For applications within the dataspace that require instant response times, such as autonomous driving or real-time analytics for financial trading, 5G’s low latency is a game-changer. It’s like having a conversation with someone in real-time, without those awkward pauses that can disrupt the flow.
Enhanced Connectivity
5G technology supports a higher number of connected devices per unit area than 4G. This capability is crucial in densely populated areas or in scenarios where many IoT devices are deployed, such as smart cities or industrial complexes. Within a dataspace, this means more devices can contribute data and insights without the network becoming congested or unreliable. Imagine a crowded concert where everyone can stream videos without buffering; that’s what 5G offers to the dataspace.
Enabling New Technologies and Applications
The combination of high speed, low latency, and enhanced connectivity allows for the development and deployment of new technologies and applications. For example, augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR), which require the quick processing of massive amounts of data, become more viable and widespread with 5G. In the dataspace, this translates to more immersive and interactive experiences, whether for entertainment, education, or professional training.
Facilitating AI and IoT Integration
5G’s capabilities boost the efficiency and effectiveness of AI and IoT within the dataspace. AI applications can process data collected from IoT devices more quickly, leading to faster insights and actions. This could mean smarter cities that adapt traffic lights in real-time to reduce congestion or manufacturing plants that predict equipment failures before they occur, minimizing downtime.
In layman’s terms, 5G acts as the high-speed highway that connects different parts of the dataspace, ensuring data flows quickly, reliably, and efficiently. This not only enhances the performance of current technologies but also opens up possibilities for new innovations that can transform our lives and work.
To watch ” JOM! lets Sembang AIoT” brought to y by AIoTmission check at the link below:
https://youtube.com/live/xfYJWqEg93M
