Progression of 1G to 5G mobile network that impacts the AIOT implementation in the industry.

This week’s live discussion offers a unique conversation, or ‘sembang,’ exploring the transformative journey of mobile networks from 1G to 5G. We delved into how these advancements in mobile communications have profoundly impacted applications of AIoT across various industries. Additionally, we touched on Malaysia’s NEW INDUSTRIAL MASTER PLAN 2030 (NIMP2030).
Manufacturing continues to serve as a pivotal growth catalyst for Malaysia. With its significant contribution to the nation’s economy, NIMP 2030 has been designed to elevate industrial capabilities to new heights. The plan is centered around key missions and enablers.
Missions:
Elevating Economic Complexity
- Paving the Way for a Digitally Vibrant Nation
- Striving for Net Zero Emissions
- Ensuring Economic Security and Inclusivity
Enablers:
Mobilizing a Robust Financing Ecosystem
- Encouraging Talent Development and Attraction
- Streamlining the Investor Journey for Business Ease
- Implementing a Nationwide Governance Framework
At Sine AIoTmission, our focus lies in fostering innovation and technological development in the realms of Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) and Artificial Intelligence (AI). Specifically, the mission of ‘teching up for a digitally vibrant nation’ and the enabler of ‘fostering talent development and attraction’ represent the facets where we are best positioned to contribute, especially in terms of digital transformation and talent cultivation.
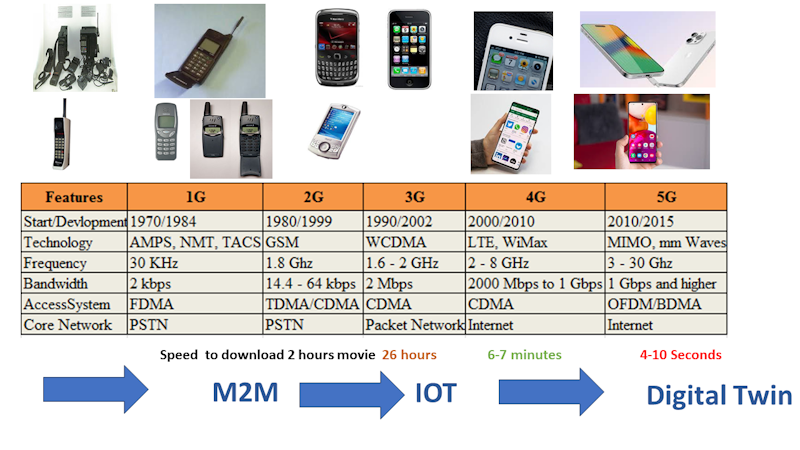
The evolution of mobile networks from 1G to 5G has brought transformative changes to the Internet of Things (IoT) applications in various industries. Each generation brought with it improved speed, reliability, efficiency, and features that greatly influenced the capabilities and spread of IoT devices. Here’s a breakdown of how each generation impacted IoT applications:
- 1G (1st Generation)
- Overview: 1G mobile networks introduced the world to cellular communication with analog voice.
- IoT Impact: There wasn’t any direct impact on IoT since 1G was primarily voice-centric. However, it set the foundation for mobile communication which would be pivotal for IoT’s evolution.
- 2G (2nd Generation)
- Overview: 2G introduced digital communication, leading to services like SMS and MMS. GSM, its most popular standard, had limited data service like GPRS and EDGE.
- IoT Impact: 2G marked the beginning of Machine-to-Machine (M2M) communication, allowing devices to exchange data without human intervention. This facilitated the earliest versions of connected devices, such as fleet tracking systems.
- 3G (3rd Generation)
- Overview: 3G brought faster data transfer rates, enabling mobile internet browsing, video calls, and mobile apps.
- IoT Impact: The improved data speeds allowed for more advanced M2M communications. IoT devices could now transmit larger packets of data more efficiently, allowing for richer applications such as video surveillance, remote health monitoring, and more responsive remote monitoring and management systems.
- 4G (4th Generation) & LTE (Long-Term Evolution)
- Overview: 4G offered even faster data speeds and lower latency, making real-time communication and HD video streaming on mobile devices possible.
- IoT Impact: The data capabilities of 4G gave rise to a vast array of IoT applications. Smart homes, smart cities, connected cars, and industrial automation became feasible. Real-time data analytics, cloud integration, and more sophisticated remote applications saw significant growth.
- 5G (5th Generation)
- Overview: 5G is characterized by ultra-high speeds, extremely low latency, increased bandwidth, and enhanced connection density.
- IoT Impact: 5G has the potential to revolutionize IoT:
- Ultra-reliable Low-latency Communication (URLLC): Crucial for applications like autonomous vehicles, industrial automation, and drone operations where split-second communication can be the difference between safe and unsafe operations.
- Massive Machine Type Communication (mMTC): This allows for a massive number of devices to be connected in a small area, essential for smart cities or densely packed industrial environments.
- Enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB): Provides high data rates for applications such as virtual reality (VR) or augmented reality (AR) in industrial training or maintenance.
- IoT in Various Industries: With 5G’s capabilities, industries like healthcare can now use real-time remote robotic surgeries, agriculture can deploy precision farming techniques using sensors and drones, and smart cities can manage resources and traffic in real time.
The evolution from 1G to 5G has expanded the horizons of IoT applications in industries from basic remote monitoring to complex, real-time data-driven operations that can transform the way industries function. As we look to the future, continued advancements in mobile networks will further amplify the capabilities and integration of IoT in various sectors
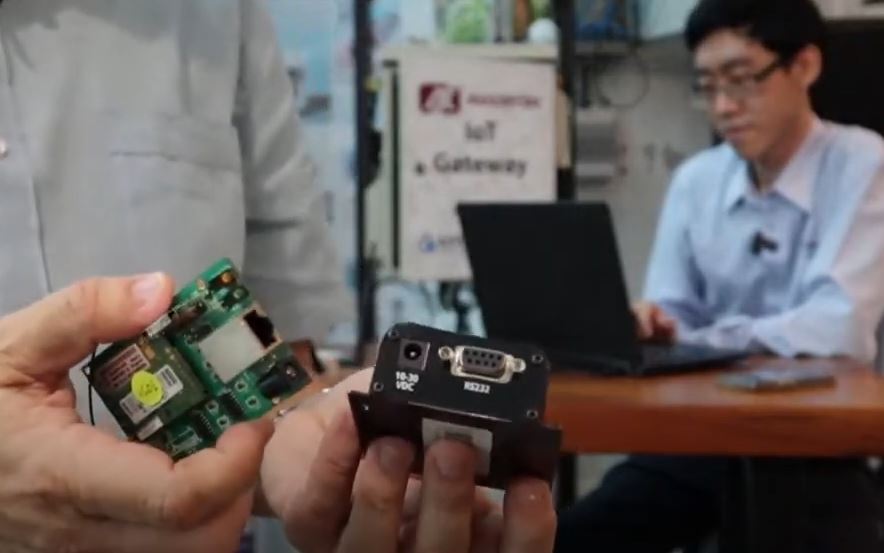

some 2G modems with conventional RS232 interface and TcPip ( LAN) interface are shown in the session where this set of legacy at some points has brought many successful applications in for remote access in many industries.
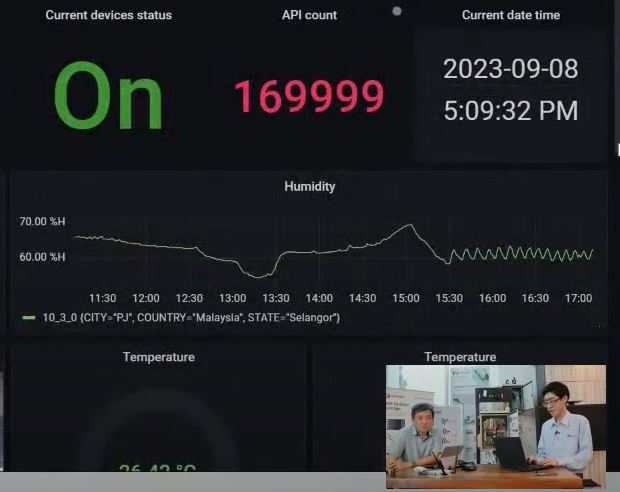
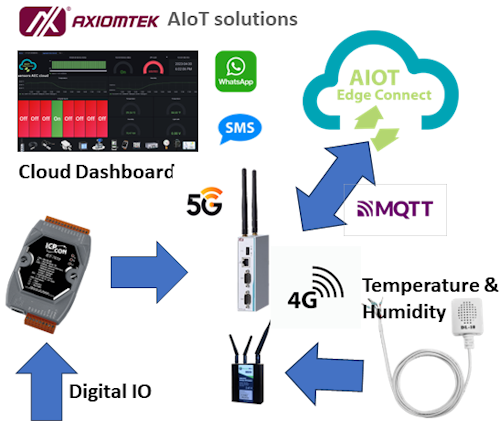
The Live demo cover the followings :
1. Onboard Modbus IO Devices to the 4G /5G gateway router
2. publish Data to the cloud
3. Visualize data on the Dashboard
4. setting Alert -Whatsapp
5. Data logging and Download
Ultimately, all the data collected will be used in the future AI Data analytic with any ready AI studio from Microsoft Azure, AWS, Google and etc.
